Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing manufacturing right now and anyone working in the industry knows how competitive the market is. Augmented reality is a combination of digital and audiovisual elements that connects the real and digital worlds, displaying an enhanced version of the world around us.
A large number of companies have taken the leap and integrated digital transformation in manufacturing operations, and this move has positively effected their bottom line.
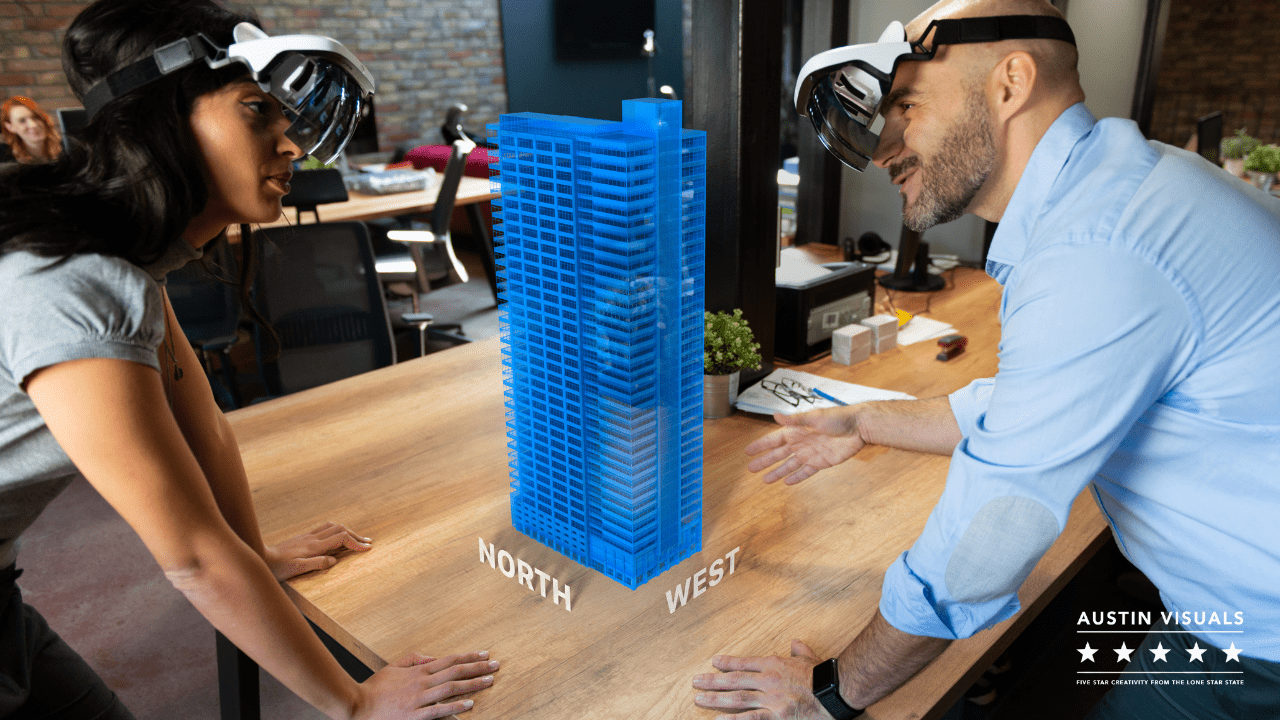
Many confuse AR with virtual reality. Virtual reality (VR) shuts out the real world in a fully immersive experience whereas Augmented Reality overlays a computer generated (CGI) video onto a camera captured video. This makes it appear that the CGI objects are in the same room with a fixed location in the real world.
This enables part of the visible surroundings to become digital and interactive. Unlike VR, Augmented Reality doesn’t require a headset that envelops the user’s entire field of vision or special controllers that translate to motions on the screen.
Manufacturing worker movements are hampered if VR was used because their real-world interaction would be blocked with the headset on. Instead, Augmented Reality devices make employee movement intuitive and seamless. Using a wearable, a worker can tap into dashboards, data, maintenance history, and 3D schemas inside a factory setting, with a digital overlay.
MarketsandMarkets predict the market for AR will reach $72.7 billion by 2024 at an annual growth rate of 46.6%. Manufacturers who want to stay competitive will increasingly embrace AR with its many use cases and benefits.
Top 5 Benefits of AR in Manufacturing
There’s a reason Augmented Reality is one of the most talked-about innovations right now. Businesses and enterprises understood its potential for entertainment products — like TikTok and Pokemon Go — and now, for those staying up-to-date with the leading technology, AR is just starting to get adopted by manufacturing companies, worldwide. Here are the top five benefits of AR in manufacturing:
1. Virtual Work Instructions & Training
Using Augmented Reality to digitally instruct workers has saved manufacturing companies time and money by standardizing the process. Instead of a worker reading a handbook or one computer screen with multiple actions AR projects work instructions directly onto the work surface, guiding workers one step at a time.
This revolutionizes the training process and instructions, reducing the delay in understanding, minimizing errors, and alleviating cognitive issues with workers.
Adding visual and audio cues into the steps creates a more comprehensible process, with less on screen words needed. Another advantage of AR in manufacturing is the drag-and-drop interface that programs these features. More time is saved when designing work instructions for manufacturing and assembly processes when companies can drag and drop 3D features into AR interfaces.
The additional sensory features like audio cues, blinking lights, animations, and videos draw attention to the instructions, which can assist in bridging language barriers. On site oral training can depend on the trainer for accuracy and paper-based instructions can vary depending on when they were updated last.
Other Uses
Augmented Reality work instructions can be updated across an enterprise with just one click. Every connected system then updates simultaneously, ensuring no lapse in information across the company.
Many firms have also reduced their waitlists for new products by digitizing the training process through Augmented Reality training apps. After being fully instructed through augmented reality in manufacturing training, often production can be ramped up once the process is streamlined. This is because AR can fully or partially replace human trainers without the need for special equipment or machinery.
2. Logistics
AR simplifies how logistics are aggregated and with remote workers, AR technology minimizes the need for employee mobility, allowing workers to stay in one location while overseeing all the vital logistics processes. The order-tracking features of AR improves the ability to track products, personnel and transport.
A company ahead of the curve already using Augmented Reality is DHL. Even today, DHL has started integrating smart AR glasses and an AR application that allow employees to minimize manual work, and reduce the probability of an error by following a logistics workflow.
3. Quality Assurance
In manufacturing, ensuring quality is tantamount. Inspections and verification often don’t take place until the end of a process. However, with guided AR solutions, digitized work instructions can implement faster inspections at any step without obstructing cycle time.
Neural Networks are used in many algorithms to enhance how quickly automated processes self-perfect while still operating. AR software even incorporates 3D vision cameras and machine learning to recognize errors like counting based on part type, proper torque, and correct wire placement.
Augmented Reality programs store all inspection information, including process data, and can provide snapshots for added assurance. Not to mention that some AR software also has a no-fault-forward step structure. What that means is that an employee isn’t able to proceed to the next step unless they are completely sure the present step is right.
4. Safety
A top priority in the manufacturing environment is safety. One way to avoid wasting additional resources is to use AR applications. It’s costly to produce technical training and education for complex machinery or dangerous equipment.
One use case for augmented reality in manufacturing safety is for logistic workers to check a connected system that informs employees where products and goods are located. AR systems can scan the information needed and help distribute the order from there. Afterwards, a worker can deliver the product to the correct location.
A maintenance staff could use Augmented Reality systems to see which equipment and hardware was in need of repair and become aware of potential errors. This AR system could show the maintenance workers operation times, date of last service, and probable sites of failure. AR would take the guesswork out of the maintenance duties, which speed up response time and repairs.
5. Prototyping & Product Development
Another way to reduce waitlists for new products is to shift from traditional design and prototyping to augmenting this task. This simplifies teamwork and communication between the parties without endless back-and-forth communications.
Higher ups inside a company can see the actual product being designed and constructed in real-time by using Augmented Reality. An administrator can then provide instant feedback and steer the process, removing the lengthy back-and-forth that typically happens.
Most manufacturing companies haven’t caught on yet to how effective AR is at trading thousands of pieces in complex assembly instructions for 3D Augmented Reality product design. With AR in place, designers can interact with their designs, and add or take away features early on in production, which saves the company more money.
Product developers can introduce 3D models of new products to the assembly line using Augmented Reality so workers can quality check these products before the launch date.
Want to add a variation to products? AR can help change product variations with a single click.
Ford Motor Company has 41 different vehicle models across the globe. On top of that there are up to 15 different styles for models like the Ford Ranger. Additionally, the different color options available for each model and individual customization mean that the variation of their vehicles can be an incredibly long list.
Having a plethora of options means that production can change in a heartbeat. In 60 minutes assembly line workers may assemble a headlight for the Ford Maverick and then the next hour the Mustang. Augmented reality enhances automotive manufacturing by making those changes instantaneous and efficient.
The manufacturing industry is adopting AR more and more as time passes. For example, Rockwell Automation, in Austin, Texas, manufactures motors, drives and connection devices and they use AR in product lifecycle and maintenance.
Whether adding digital work instructions, streamlining training, safety, maintenance, logistics, quality assurance or prototyping and product development – Augmented Reality is here to stay. It’s clear that AR is the future of manufacturing and key to helping productivity and efficiency skyrocket.
Want to Work With Austin Visuals to Build Your AR?
Email Us: [email protected]
Call Us: (512) 591-8024
To request a FREE quote simply fill out the form below or CLICK HERE!